
(For Product Managers) Fundamentals of LLM and Understanding LLM-Based Service Planning
arigaram
Describes the need for LLM, its technical background, and basic concepts.
입문
NLP, gpt, AI
Problematization (문제화) is a term also translated as problem posing, problem framing, problem setting, or problem definition. This concept involves questioning known facts (like requests or common sense) from a new perspective, defining the problem, and devising methods to solve it. Problematization should be the starting point for all development, yet it remains insufficiently discussed within the field. Performing projects or developing programs is, in essence, planning to solve problems. This means they are related to problematization. To solve a problem, it must first be clearly defined. However, problems are mostly presented as vague requests. Therefore, the ability to transform vague requests into clear problems is essential to reduce unnecessary 'development waste,' facilitate smooth collaboration, and accurately grasp users' true needs. This lecture helps train 'the thinking of problem construction' through practical examples and tools.
32 learners


How to uncover the real issues in requests, requirements, user feedback, and code reviews
How to formulate real problems into structured problems using problem statement formulas, etc.
How to find the root cause of the problem
A philosophical concept, 'problematization,' discerning essence from phenomena
Various tools for 'problematization'.
A starting point for collaboration, requirements analysis, and code reviews for new and junior developers!
From a PM/PO perspective, essential skills to recommend to all team members to prevent 'development waste'!
Foundational skills related to collaboration tools, soft skills, problem-solving abilities, and more!
"The project proposal is too vague, so I don't know what I'm supposed to create."
"I received feedback in the review, but I don't have a clear sense of exactly where I need to make changes."
"Now that I'm about to write the code... what was I trying to solve again?"
"When I asked a question, they responded with 'So what's the problem?'"
The core of all this confusion is because we failed to define the problem accurately. Developers constantly face problems. However, proper solutions can only begin when we can look at those problems accurately and define them properly.
Ambiguous Requirements: New developers often receive unclear requirements in projects. For example, when given vague instructions like "create a widget," they become confused about what specific functionality needs to be implemented. According to developer-focused blogs, new hires experience confusion due to "vague instructions" and lack of sufficient guidance (codeanywhere.com).
Lack of experience: With limited work experience, they struggle to systematically break down problems or independently find necessary information. As a real example, one junior developer had difficulty determining how much they should try to solve on their own and learned to ask questions only after attempting to resolve issues for excessively long periods (rachsmith.com). This uncertainty leads to anxiety (imposter syndrome), which hinders learning and collaboration.
Communication Gap: Without sufficient domain knowledge or business context, it's impossible to accurately identify the core issues in requirements. The development community also points out that lack of domain knowledge leads to requirement misunderstandings (kedin.com), which in turn results in incorrect implementation and rework.
Practical thinking methods for clarifying ambiguous requirements and defining core problems
Questioning Techniques to Extract Problems from Requirements
5 Criteria That Make a 'Problem' Truly Problematic
The skill of building rapport with other team members through communication
Schematic methods for 'defining' and 'structuring' problems
The skill of asking precise clarifying questions during code reviews, planning meetings, and task handoffs
15 Key Patterns

When what the client or planner said is too vague and you don't know what to build
Example: "The UX is not great", "It's slow", "Please make it more intuitive"
→ A state lacking the power to transform requests into problems
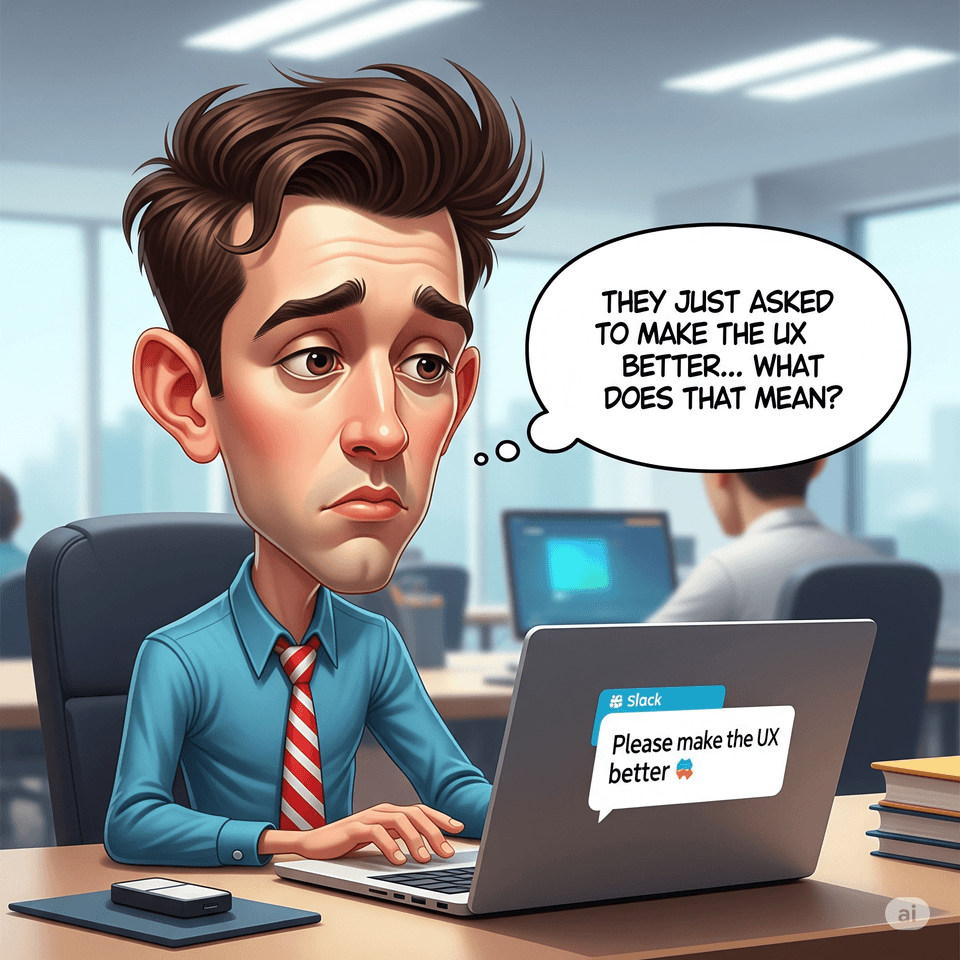
Request: "Please make the UX better"
Response: "They're just asking me to make the UX better.....what does that even mean?"
"Have you ever been stumped by the phrase 'just make it more intuitive'? The skill of turning vague requests into clear problems starts now."
The ability to analyze and structure problems is not yet familiar
When you remain at the level of just taking down what the planner says
→ Need skills to define problems independently
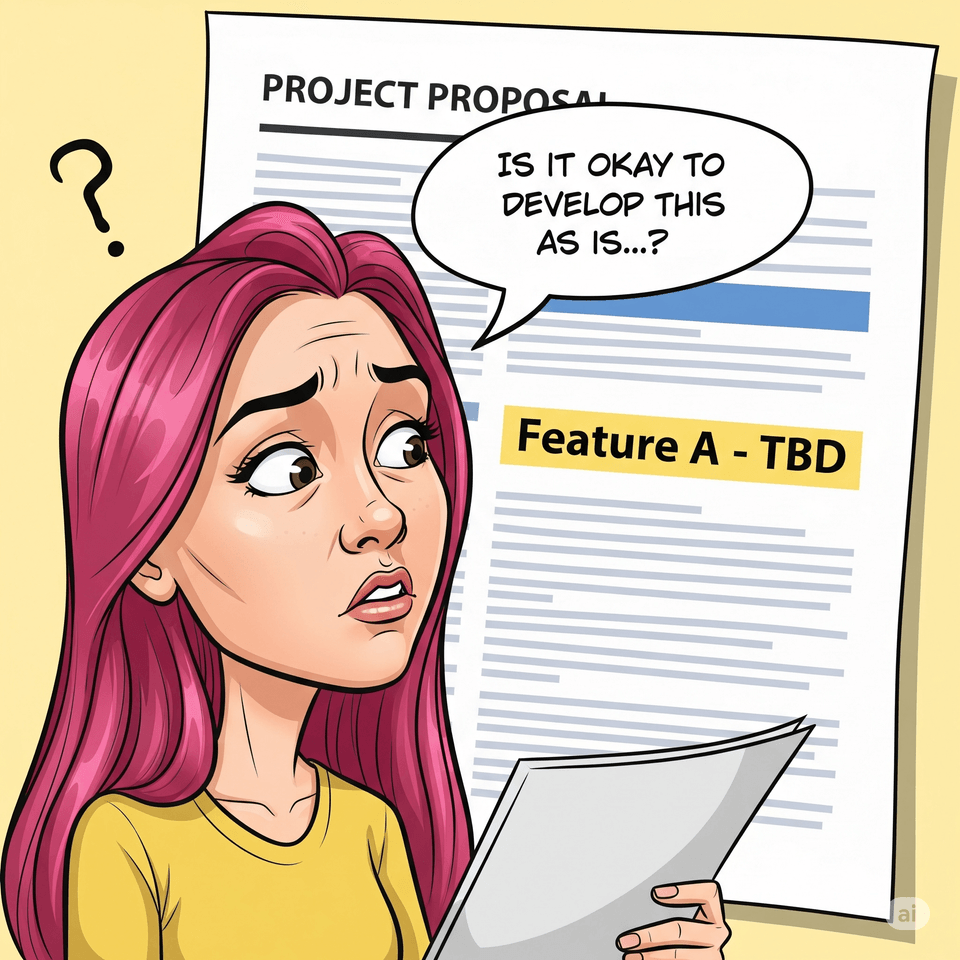
Request: 'OO' feature - currently undecided. Will be determined soon.
Response: "Is it okay to proceed with development in the current state where several features remain undecided?"
"Are you just building what you're told to build? Grow into a developer who can interpret plans and define problems on their own."
Good at implementing features, but can't explain why those features are needed
There are difficulties in designing the purpose and problem context of development
→ Developer → Problem Solver → Someone Growing to Become a Problem Setter
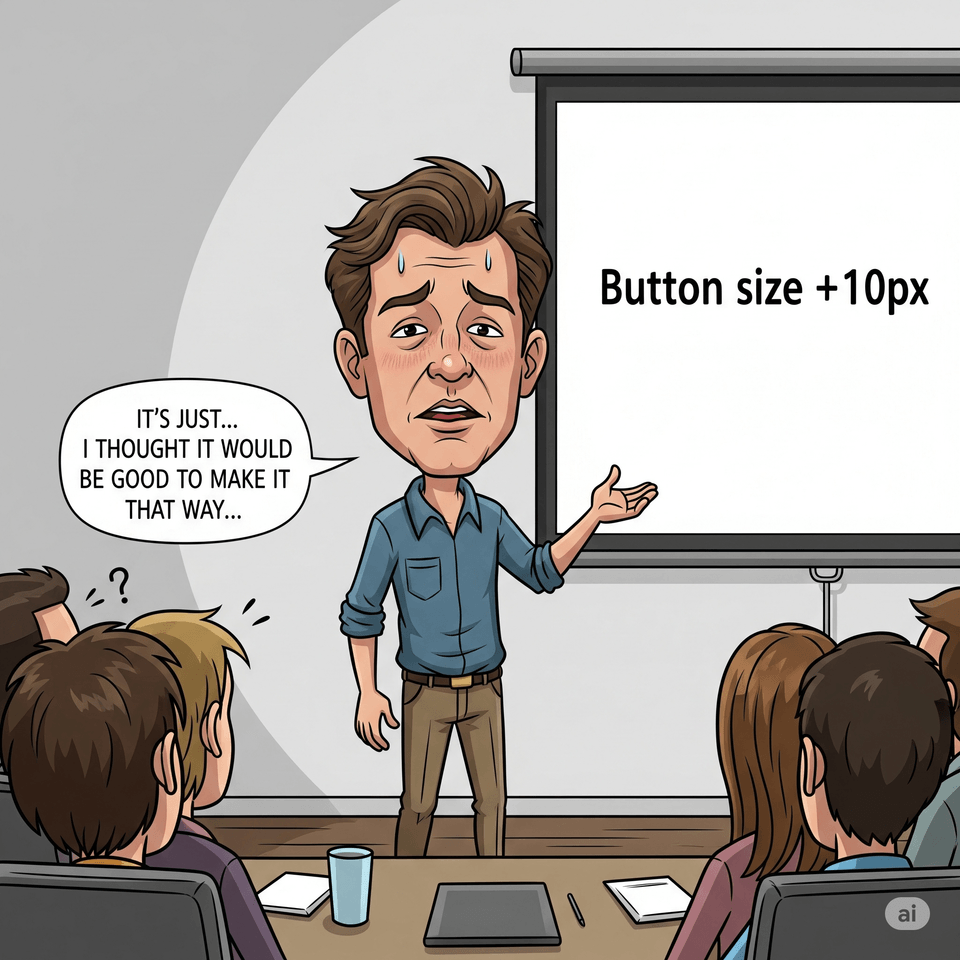
Request: Button size + 10 pixels
Response: "Well... I just thought it would be good to make it that way..."
"If you can implement features but can't explain why? Now is the time when you need thinking that penetrates to the essence of problems."
There's a lot of talk going around, but no consensus is formed on "what the problem actually is"
Feedback is repetitive, or communication conflicts occur frequently
→ People who want to structure different languages and establish a foundation for collaboration
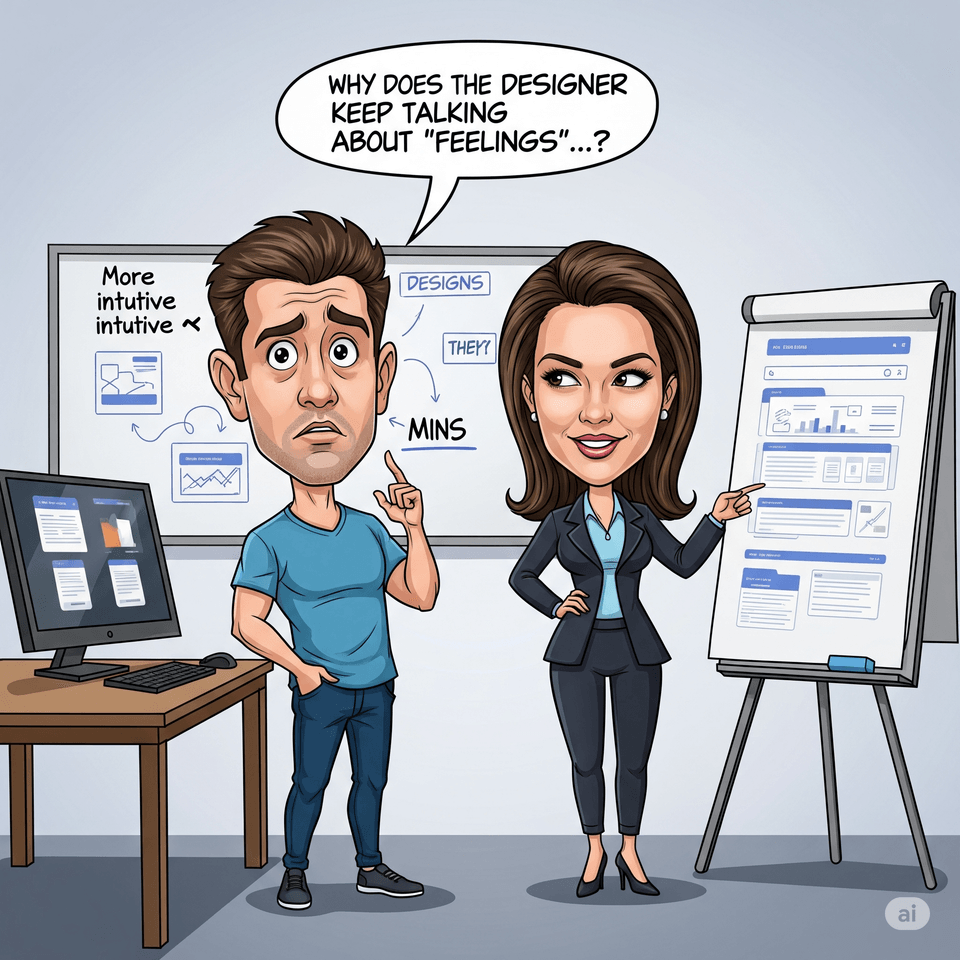
Request: "Please make it feel more intuitive"
Response: "Why do designers always talk about some kind of 'feeling'...?"
"Do you feel like you can't communicate with planners? When you organize each other's language into 'problems,' collaboration changes."
A developer growing into a role that should define problems and provide direction
The ability to structure vague requests into actionable team tasks is needed
→ Problem setting is the beginning of leadership
Request: According to the structure of [Information Request > Cause > User Situation]...
Response: "How should we define this to make it a team assignment?"
"The ability to structure vague requests into actionable tasks is your first step toward becoming a developer who leads a team."
This course is essential for all developers who have the concern of "I can write code, but I don't know what to build."
Especially for junior developers from entry-level to 3 years of experience, this can be considered an essential skill.
Requirements Gathering Questions: Posts asking "How do you gather and analyze requirements?" from newcomers and job seekers frequently appear on developer forums or Reddit. For example, a computer science student sought advice from senior developers, asking "How do you collect stakeholder requirements in practice?" (reddit.com). This shows the demand for learning how to obtain clear requirements in real projects.
Role Emphasis: According to advice from mid-level developers, the core of software development is "Problem definition", and it is mentioned that true experts need the ability to accurately define requirements (medium.com). Opinions emphasizing the importance of problem definition like this are frequently found in developer communities as well.
Educational Necessity: Korean developer blogs identify problem definition ability as a "fundamental skill"(medium.com), pointing out that defining the problem to be solved is essential before using tools when analyzing data or designing systems(inflearn.com, velog.io). These articles highlight the necessity of problem definition skills for learners.
Practical-based thinking approach:
Structured around real problem cases encountered in actual collaboration
Short and Clear Lectures:
Each lesson is typically structured to be within 10 minutes (with some exceptions), enabling highly immersive learning
Structured Thinking Training:
A slide-focused lecture that visually organizes the 'thought process' for defining problems
Practical Examples:
Recording conversation methods that turn vague feedback and abstract planning into clear problems
What is Problem Setting – The Starting Point of Problem Solving
Ambiguous requests, where did it go wrong?
5 Criteria That Make a Problem Truly a Problem
The Art of Asking "So What's the Problem?" Differently
Code reviews, planning, schedule coordination… all the moments where problem definition is used
You can structure and organize even confusing requests on your own
You can become a developer who gets to the core with just one question
You can reduce unnecessary misunderstandings during work collaboration and lead accurate conversations
Review feedback can also be converted into solvable problems rather than simple criticisms
A developer's work always starts with receiving a 'request'. However, most requests are vague and ambiguous. If you can't turn this into a precise problem, the planning goes awry, development goes in circles, and schedules get delayed.
Example: "Please make the button a bit bigger" →→ Why? For whom? What's the problem?
The most difficult part for new developers or juniors is not simple implementation, but the ability to determine 'what should be implemented'. This course addresses exactly that point.
Requirements analysis, code reviews, communication, discussions with PMs… all of these require good problem definition for smooth flow. This course trains you in the thinking method of listening and extracting the essence.
Rather than theory without practice, we provide problem statement formulas, feedback criteria, and questioning techniques that you can immediately apply in real work situations.
In summary, this course helps you become a developer capable of clear judgment and communication who doesn't stop when faced with questions like "Why do we need to develop this?" and "Is this really a problem?"
🎯 In today's developer market, 'developers who can think' like this grow the fastest.
Now, become a developer who excels at problem definition rather than just problem solving.
You must be able to see problems accurately before solutions and growth can begin.
Who is this course right for?
A developer who wants to foster the ability to independently think and determine what the true problem is, rather than just implementing given requests.
Planners, Designers, PM/POs aiming to set team direction amid vague requirements and opinions, and communicate smoothly with developers.
569
Learners
29
Reviews
2
Answers
4.5
Rating
17
Courses
IT가 취미이자 직업인 사람입니다.
다양한 저술, 번역, 자문, 개발, 강의 경력이 있습니다.
All
72 lectures ∙ (17hr 16min)
Course Materials:
All
2 reviews
5.0
2 reviews
Reviews 326
∙
Average Rating 5.0
5
The audio quality isn't great, but it doesn't interfere with studying and the content is good
Thank you. I will re-record existing lectures in the future to improve the audio quality.
$42.90
Check out other courses by the instructor!
Explore other courses in the same field!