글로벌 저자 & 리눅스 시스템 소프트웨어 개발자 (Arm, RISC-V 아키텍처)
국내 시스템 소프트웨어 분야에서 전무후무한! 'Arm 아키텍처(Armv8-A, Armv7-A)'와 '리눅스 커널' 책을 쓴 저자(2권의 책 모두 대한민국 학술원 우수도서에 선정)이며, 국내 최초로 해외 출판사(Packt)를 통해 "Reverse Engineering Armv8-A Systems" 책(영어)을 집필한 글로벌 저자입니다. 무엇보다 최신 시스템 소프트웨어 트렌드(전기자동차, 시스템 반도체- 시스템 소프트웨어)를 가장 잘 알고 있는 현업 개발자입니다. 또한 시스템 소프트웨어 분야에서 가장 지식 전파 활동을 활발하게 하는 교육자입니다.
'Reverse Engineering Armv8-A Systems: A practical guide to Kernel, Firmware, and TrustZone analysis' 책(영어) 저자, (Packt 출판사)
'시스템 소프트웨어 개발을 위한 Arm 아키텍처의 구조와 원리'(2024년, 대한민국 학술원 우수도서상) 저자
'디버깅을 통해 배우는 리눅스 커널의 구조와 원리' (2021년, 대한민국 학술원 우수도서상) 저자
'프로그래머스 데브 코스: 리눅스 시스템 및 커널 전문가' 메인 강사
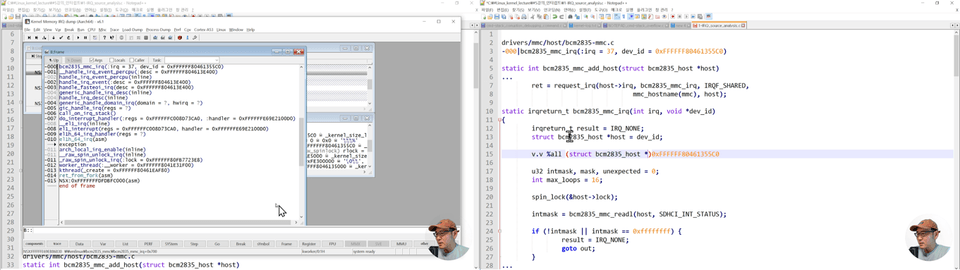
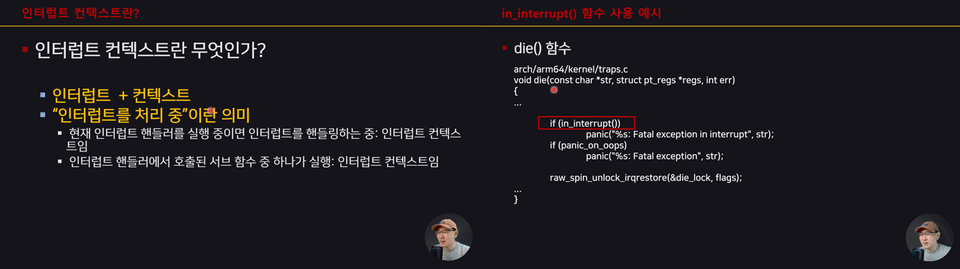
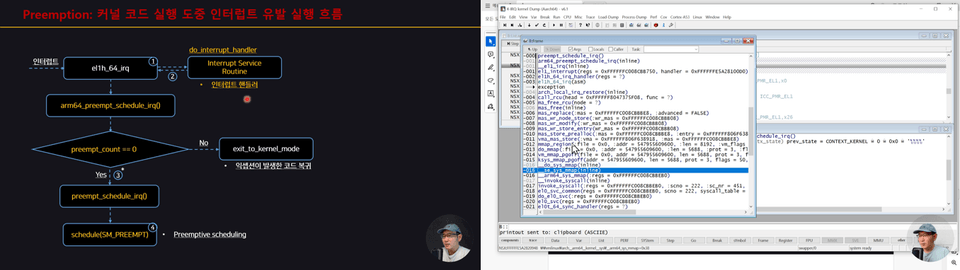
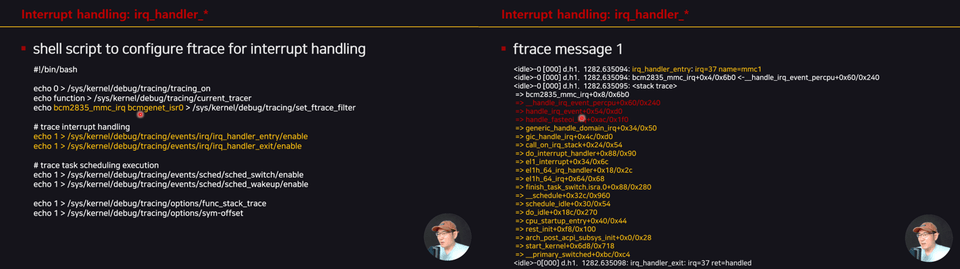
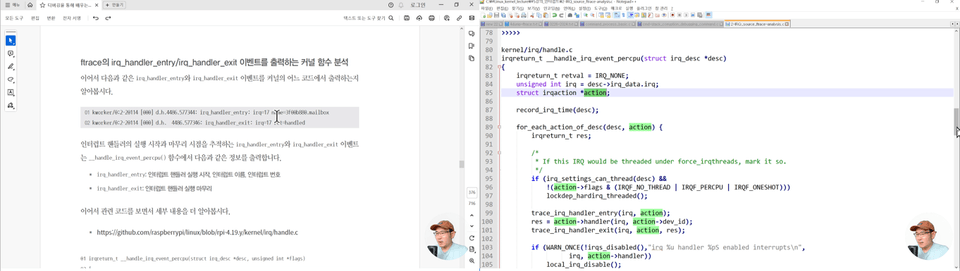
2022년 6월, 한국컴퓨터종합학술대회 (KCC2022) - 튜토리얼 발표 [ftrace를 이용해 리눅스 커널 정복하기]
LG전자 '리눅스 커널' 및 'Armv8 아키텍처' 사내 강사(국내 및 해외 개발자 포함) - (2020년~현재)
국내에서 어느 누구보다 리눅스 커널과 Arm 아키텍처(Armv8-A, Armv7-A)를 잘 설명할 수 있는 교육자라고 자신있게 말씀드릴 수 있습니다.
강의문의 : austindh.kim@gmail.com
주요 로드맵 🎯
'시스템 소프트웨어 개발자를 위한 Arm - basic course'
'시스템 소프트웨어 개발자를 위한 Arm - advanced course'
시스템 소프트웨어 개발자를 위한 Linux kernel - basic course










![Linux Introduction and Linux Kernel Overview [Author's Direct Lecture Part 1-1]강의 썸네일](https://cdn.inflearn.com/public/courses/333097/cover/8e09c5df-0571-462e-878c-39ddf13549b6/333097.png?w=420)
![Linux Kernel Structure and Principles: Interrupt Bottom Half [Author's Direct Lecture Part 1-6]강의 썸네일](https://cdn.inflearn.com/public/courses/333195/cover/3b8c8cd2-44b0-43b7-a441-b950ba367717/333195.png?w=420)
![Linux Kernel Structure and Principles: Processes [Author's Direct Lecture Part 1-4]강의 썸네일](https://cdn.inflearn.com/public/courses/333193/cover/442053bf-cf8d-4d79-a009-41654b6eb262/333193.png?w=420)
![Linux Kernel Structure and Principles: Debugging - Advanced Practice [Author's Direct Lecture Part 1-3]강의 썸네일](https://cdn.inflearn.com/public/courses/333192/cover/bc7d9889-21ec-44d7-bcb0-10452507d7b3/333192.png?w=420)

![Linux Kernel Structure and Principles: Workqueue [Author's Direct Lecture Part 1-7]강의 썸네일](https://cdn.inflearn.com/public/files/courses/333196/cover/01k29sce7t2gm6wzc39gppy1cf?w=420)
![Linux Kernel Structure and Principles: Debugging - Basic [Author's Direct Lecture Part 1-2]강의 썸네일](https://cdn.inflearn.com/public/courses/333148/cover/a6c28b23-47d5-452e-8b62-5ba8c769f904/333148.png?w=420)
![Arm Architecture: Cache [Author's Direct Lecture Part 3-4]강의 썸네일](https://cdn.inflearn.com/public/courses/332870/cover/a76af7ed-15da-452d-960a-9a5503a78c24/332870.png?w=420)
![Arm Architecture: Memory Management (MMU) [Author's Direct Lecture Part 3-5]강의 썸네일](https://cdn.inflearn.com/public/courses/332864/cover/18186c49-1c49-40e1-acd0-b0603efddb80/332864.png?w=420)
![Arm Architecture: Virtualization [Author's Direct Lecture Part 3-2]강의 썸네일](https://cdn.inflearn.com/public/courses/332863/cover/ff1b9cef-935e-4da6-a62e-1386e203b37c/332863.png?w=420)
![Arm Architecture: Memory Model and Barriers [Author's Direct Lecture Part 3-3]강의 썸네일](https://cdn.inflearn.com/public/courses/332809/cover/418b1d01-d4bf-4e57-8f86-895978f719ba/332809.png?w=420)
![Arm Architecture: TrustZone [Author's Direct Lecture Part 3-1]강의 썸네일](https://cdn.inflearn.com/public/courses/332739/cover/000c70cc-3a46-4f03-87f0-02f16dbf9b1e/332739.png?w=420)