![[입문] Qt 6 프로그래밍 2편강의 썸네일](https://cdn.inflearn.com/public/courses/326823/cover/9c839f33-d59f-422a-9704-64534673a39c/커버이미지_Qt 6 프로그래밍_2편.png?w=420)
[입문] Qt 6 프로그래밍 2편
김대진
이번 강의는 Qt 프로그래밍 1편에 이어서 2편 강의 입니다. Qt를 처음 접하시는 분들은 1편을 먼저 학습하시고 2편을 학습하는 것을 권장합니다.
입문
Qt, GUI
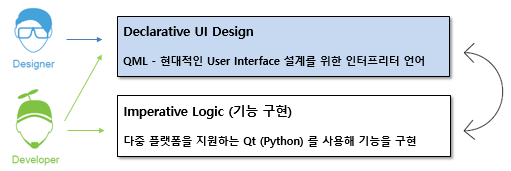
QML is a programming interpreter language for creating UIs provided by Qt. It is similar to JSON and can use JavaScript. Using QML and Python together, you can easily develop modern, advanced UIs.

Basic syntax of QML and utilization of UI components: Understand the syntax, structure, and types of QML and learn how to design various user interfaces by utilizing basic UI components based on them.
Implement advanced UI features: Learn how to implement more vibrant, advanced UIs with dynamic UI, animation, state transitions, and more, and how to leverage animation and easing curves to deliver natural, smooth user experiences.
Developing Scalable Applications with Python Integration: Understand the data exchange and interoperability between QML and Python, and learn how to build flexible and scalable applications by extending and integrating QML types with Python.

Qt Framework UI implementation,
More powerful with QML!

Modern, advanced UI in the Qt framework
It is a programming language that is easy to develop in.
QML (Qt Modeling Language) is a powerful programming language provided by the Qt framework, providing an optimized solution for UI development. It enables the efficient implementation of modern, sophisticated, and advanced user interfaces, and easily supports intuitive and flexible design and animation tasks, contributing to a maximized user experience.
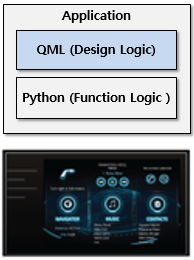
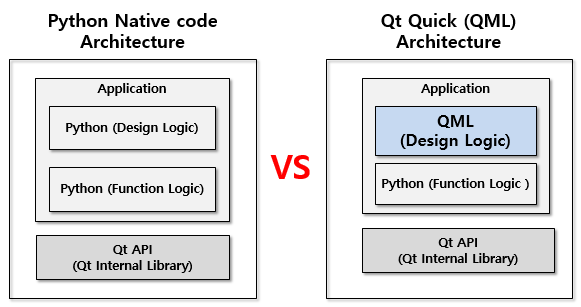
When developing a GUI with the Qt framework, you can clearly separate UI design logic (QML) from functional logic (Python). Specifically, QML can be utilized as a dedicated language for UI design logic. Implementing a UI using QML allows for a complete separation of design logic and functional logic (Python), maximizing code reusability and improving maintainability.
Developing design logic using QML allows for much simpler and faster UI implementation. Furthermore, it allows for easy application of modern, advanced GUI technologies like Flickable, Gesture, Animation, and 3D, making it an excellent choice for creating sophisticated and intuitive user experiences.
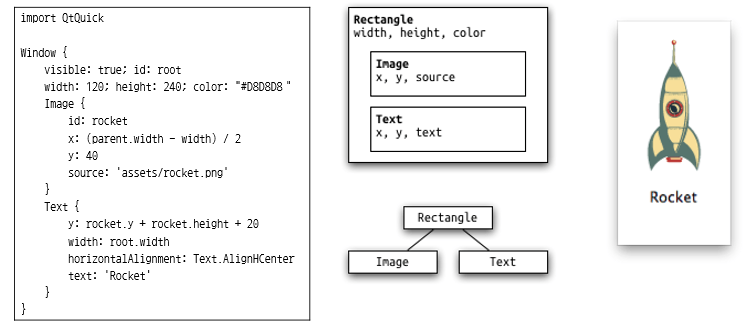
Let's look at a "Hello World" output example, a common example when first learning a programming language. It's easy to see how concise QML is.
import QtQuick
Window {
width : 300
height : 200
visible : true
title : qsTr ( "QML Example Source Code" )
Text {
x : 80
y : 70
text : "Hello World"
font. pixelSize : 25
}
} 
QML example source code execution screen
QML is a concise and intuitive language, accessible enough for even non-developers to understand. This allows designers and developers to communicate seamlessly, share ideas effectively, and collaborate based on QML code.
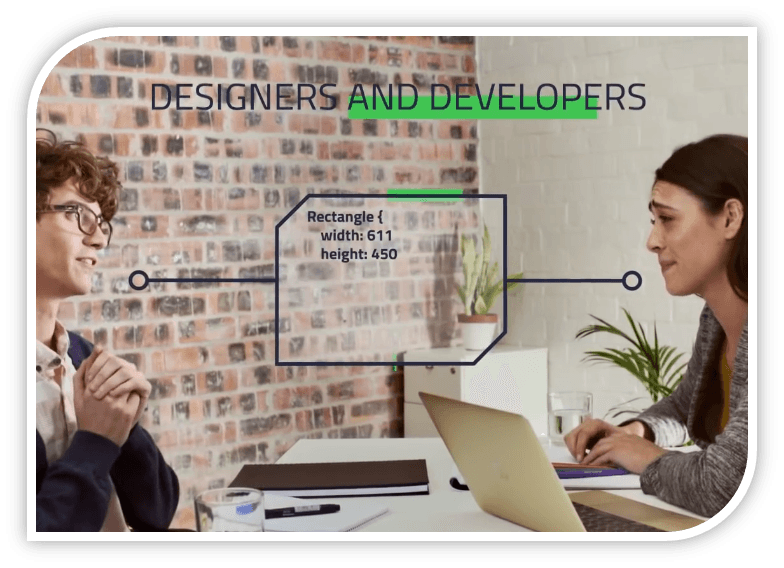
Therefore, by utilizing QML, designers and developers can collaborate based on the same development tools, shortening the development period more efficiently than before.
Advanced UI/UX implementation
Anyone (developers, designers) who wants to easily implement modern, advanced UI/UX using QML in Qt

Source code reusability
By separating design logic and functional logic, you can increase source code maintainability and reusability.
Desirable collaboration
Designers and developers can communicate and collaborate effectively through the same tools as QML.

Intuitive and modern UI development
Recommended for those who want to build vibrant and smooth user interfaces using QML.
Develop flexible applications with Python and QML
Ideal for developers looking to build scalable applications across multiple platforms.
Maximize animation and user experience (UX)
Recommended for those who want to learn advanced animation techniques to make their UI more natural and attractive.
Learn how to develop modern, advanced UX/UI using QML.
You will learn how to use QML to completely separate design logic (QML) from functional logic (Python).
You can naturally learn QML development skills required in the field by studying the theory by section and writing code yourself based on various practical examples.
A lecture that considers real-world situations
The course is structured to enhance practical skills. After each section's theoretical study, you'll learn through hands-on practical examples, allowing you to enhance your practical skills.
Beyond the online walls
We've captured the image of a knowledge sharer on the screen. Learn anytime, anywhere, as if you were taking an offline class, with vivid live coding.
Section 1. Starting the lecture
Before the lecture begins, this section provides an overview of the entire learning process. This section introduces the instructor and summarizes the key content covered in each section, helping you grasp the overall flow of the lecture.
Section 2. Lecture Materials
This section provides all the example source code files used in the lectures, starting in Section 3 , in a compressed file for download. This section is provided for reference purposes only, not as part of the course.
Section 3. Setting up the development environment
This section delves into how to set up a development environment for Python programming using Qt. We'll also explore how to use Visual Studio Code as an IDE for writing source code.
Section 4. What is QML
QML is an interpreted language provided by the Qt Framework. In this lesson, we'll explore the features and advantages of QML.
Section 5. Syntax and Structure of QML
This section covers the structure and syntax of QML, and how to use QML through practical examples.
Section 6. Type
Type is a concept similar to QWidget in Qt. In this section, we'll learn what Type is, focusing on the most frequently used types provided by QML. As a practical example, we'll implement a button type using the Accessible type and report on it.
Section 7. Event
This section covers how to implement event handling for user interface events, such as touch, mouse, and keyboard input. You'll also learn how to implement signals in QML. In this hands-on example, you'll learn how to handle signals in detail through examples of connecting signals to methods (functions).
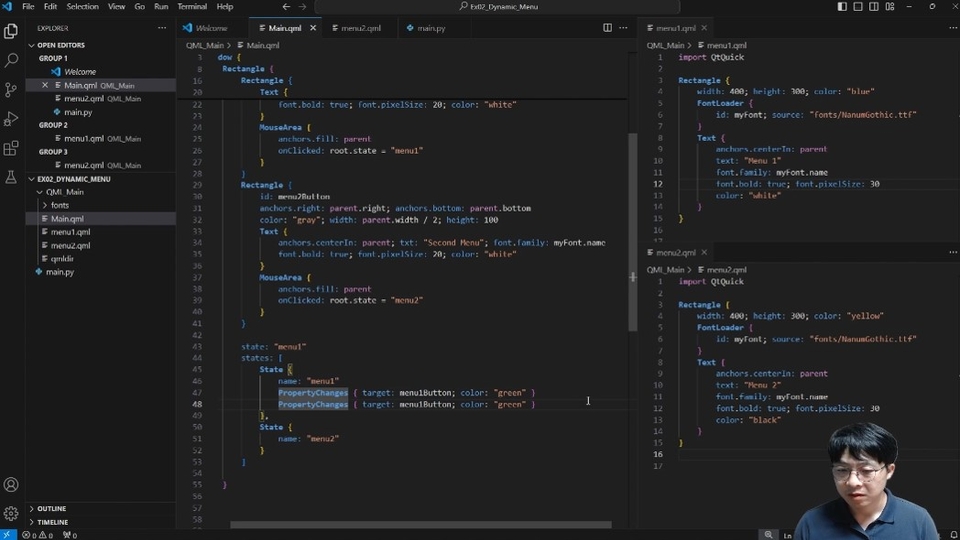
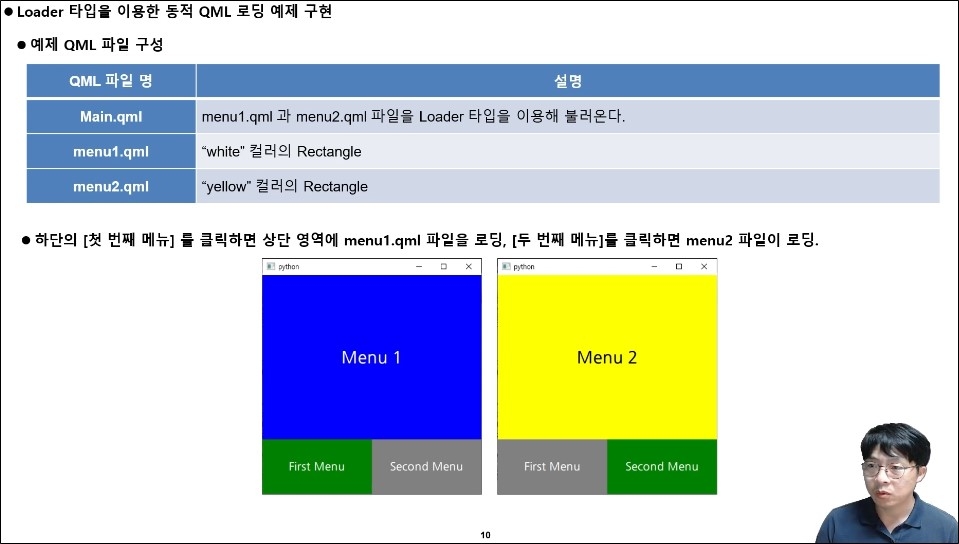
Section 8. Implementing Dynamic UI using Loader type
You'll learn how to dynamically change specific areas of a UI. For example, you'll learn how to transition from GUI screen A to screen B when a certain condition is met. Therefore, in this section, you'll learn how to dynamically implement screens. The final hands-on example will demonstrate how to dynamically change screens using the Loader type.
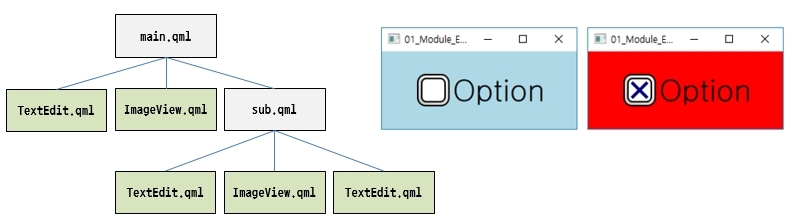
Section 9. Module Programming
Learn how to modularize user-defined types, such as frequently used GUI modules like buttons and combo boxes. You'll also learn how to modularize and implement QML through hands-on examples.
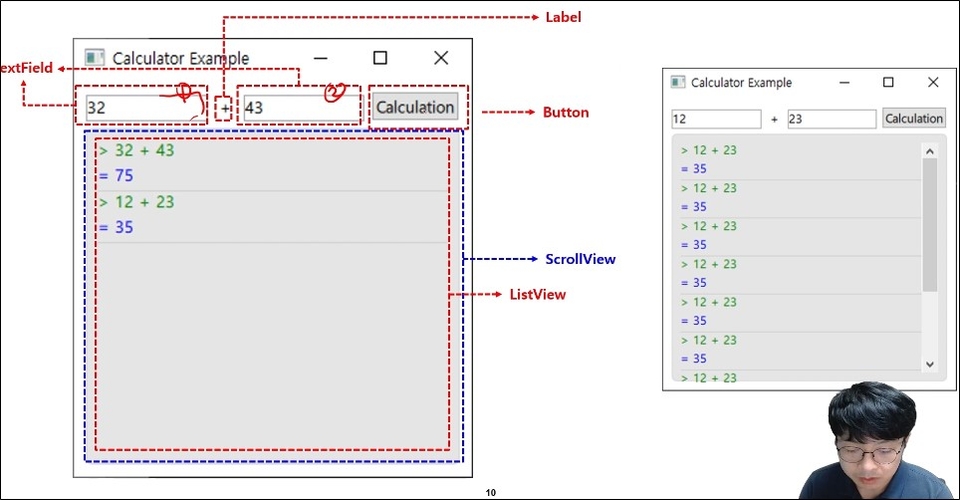
Section 10. Using JavaScript in QML
Learn how to use JavaScript functions in QML and how to import JavaScript files in QML. In this hands-on example, you'll learn more about using JavaScript by implementing a calculator.
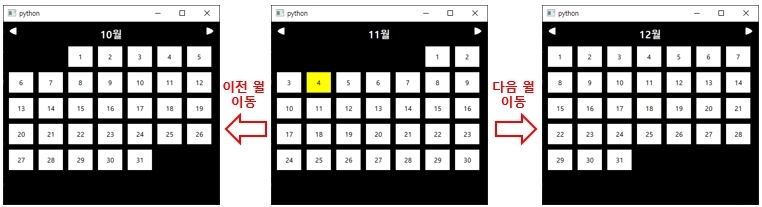
Section 11. Type Positioning
Type Positioning teaches you how to display types on the screen. For example, you'll learn how to arrange types horizontally, vertically, or in a grid-like pattern. You'll also learn how to retrieve information about a specific type when multiple types are arranged sequentially.
Section 12. Anaimation
Animations provide an easy way to apply animations to GUI elements. For example, a button might appear and disappear. Animations can be used for this. A button might disappear for one second, for example, or a specific amount of time can be given for the Opacity value to change from 100% to 0%.
Using these animations, you can create effects similar to those used on GUIs. You can also implement effects that allow smooth screen transitions. Therefore, in this section, you'll learn how to use animations on GUI elements.
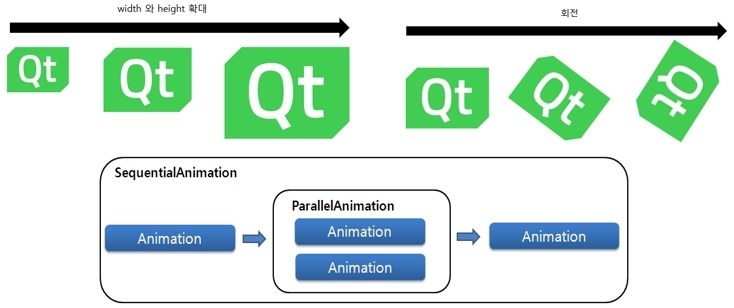
Section 13. Ball Bounding Example Implementation Using Animation and Easing Curves
Easing Curves allow you to create more sophisticated effects by using specific options within your animations. For example, by accelerating a specific time interval during a 10-second animation, you can create a variety of effects.
In this section, you will learn how to use easing curves in animations through practical examples.
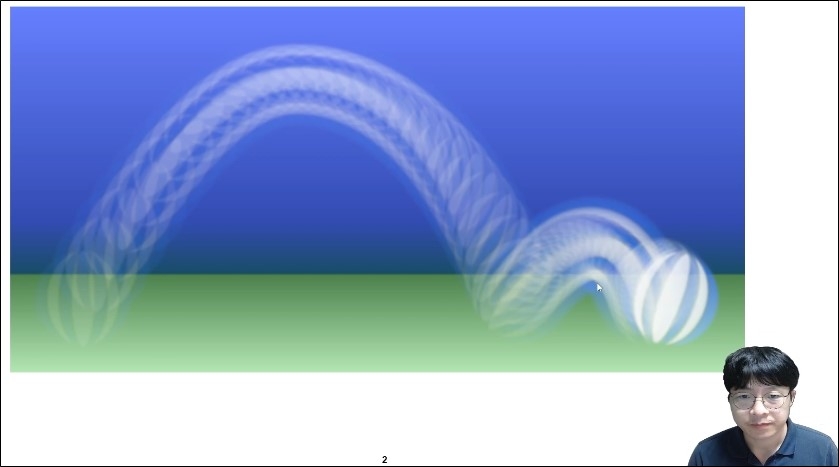
Section 14. State and Transition
A state represents a condition. A transition represents an action. For example, in an on/off switch, the conditions are "ON" and "OFF," and the action (transition) is defined as the change from "ON" to "OFF." Using states and transitions, you can group complex behaviors and have them change collectively when the conditions change, making complex GUI implementations easier to implement.
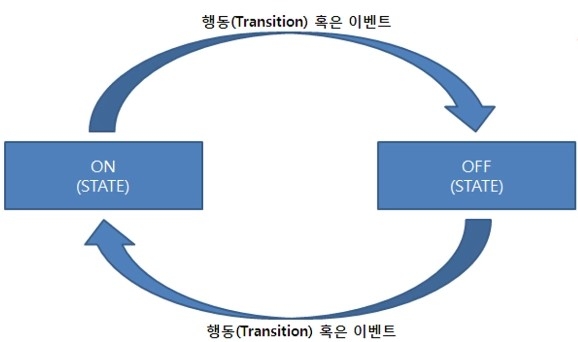
Section 15. Implementing an Image Viewer Example Using State and Transition
In this section, we will implement an Image Viewer using the State and Transition learned in the previous section.
Section 16. Model and View
Models and Views are used to display large amounts of data on a GUI. For example, when displaying 100 data items in a table, the data is stored in the Model, and the View represents how the data stored in the Model is displayed on the GUI. The View can be a table or a tree. In this section, you'll learn how to use Models and Views.
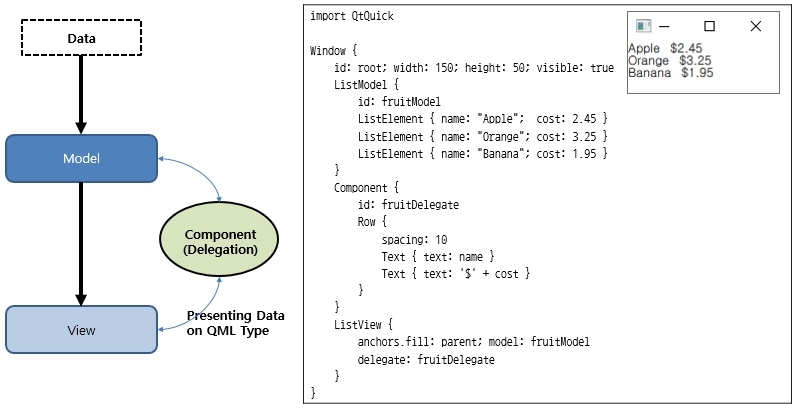
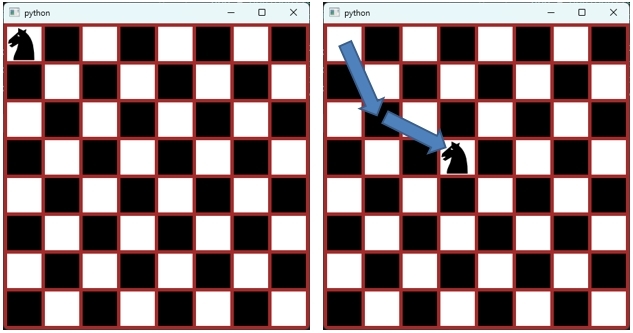
Section 17. Implementing a Chess Game Using Model and View
We will learn in depth how to implement a Knight in the Chess Game using Model and View as an example.
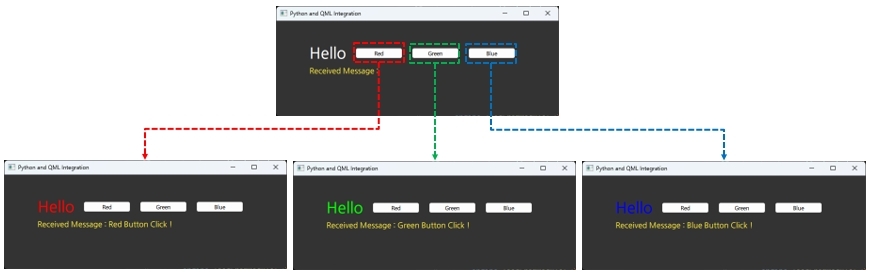
Section 18. Integration between QML and Python
Learn how to call functions in specific Python classes from QML and how to call specific JavaScript functions from Python in QML. You'll also learn how to call functions and pass data between QML and Python through hands-on examples.
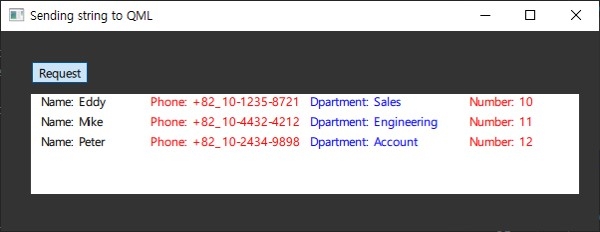
Section 19. Exchanging List Data Between QML and Python
Learn how to pass large lists of data from Python to QML. And with a practical example, you'll learn how to process data stored in a Python list, pass it to QML, and display it on a UI.
Section 20. Implementing a New QML Type Using Python
Just as we used QPainter to display 2D graphic elements on QWidget, we will learn how to use the QQuickPaintedItem class provided by Python to display 2D graphic elements on QML Type using QPainter.
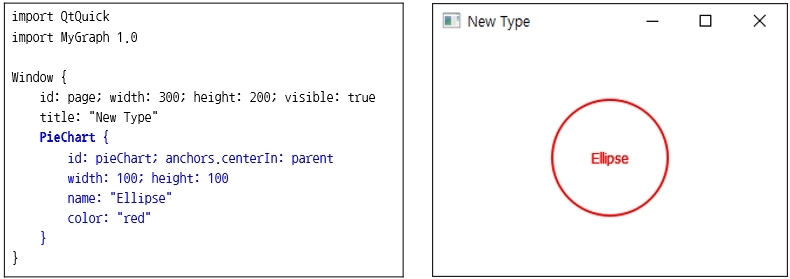
Section 21. Implementing QML types in nested structures
When simply implementing a Type, you may need to implement a hierarchical structure. For example, you may need to implement multiple Types within a Type. In this section, we'll learn how to implement a hierarchical Type through the topic of Chart.

👉 See how you've changed after learning.
After taking this course, you'll be able to use QML fluently. You'll also understand the differences and pros and cons of using QML in real-world projects versus the traditional Python/Qt approach, QWidget.
Additionally, when implementing a project using QML, you can completely separate the design logic (QML part) and functional logic (Python) of the implemented source code, which increases the reusability of the written code.
Before taking the course, write down at least three questions and answers that prospective students might have.
We encourage answers that reveal the knowledge sharer's personality rather than obvious or formal answers.
Q. In addition to theory and grammar, will I be able to access a variety of practical examples?
Yes, you can. After each section's theoretical lecture, you'll have a hands-on coding session with the instructor, using examples. This allows you to learn practical programming skills using QML in the workplace.
Q. Are there any reference materials or textbooks for the lectures I am studying?
I currently serve as an administrator for the Qt Developer Community ( qt-dev.com ). You can find additional resources related to Qt and QML on this site.
Q. Is there anything I need to know before attending the lecture?
This course requires basic knowledge of Python and Qt. If you don't have any experience with Qt, we recommend taking the previous course, " [Level 1] Python Programming with Qt: Introduction, " before taking this course.
Q. What level of content is covered in the class?
Covers everything from QML basics to advanced topics for various application areas.
Operating System and Version (OS): This course is conducted on the Windows operating system, but can also be used on various other operating systems, including macOS, Linux, and Ubuntu. However, we recommend using Windows.
We've set aside time during class to install the software needed to build a development environment, so all you need to bring is a computer and operating system.
After taking the course, you can download all the example source code for this course in Section 2 as a study reference.
If you have any questions or concerns during class or anything you don't understand, don't hesitate to ask. The process of discussing and resolving issues together is incredibly beneficial to your learning.
Who is this course right for?
Anyone interested in developing intuitive and modern UI
Anyone who wants to create flexible applications through integration of Python and QML
Anyone who wants to maximize user experience through animation and dynamic UI implementation
Need to know before starting?
Basic Python programming knowledge: You need to understand Python's basic syntax and data structures (lists, dictionaries, etc.), function definitions, and calls. With this basic knowledge, you can easily approach programming using Qt.
1,065
Learners
102
Reviews
104
Answers
4.7
Rating
9
Courses
근무경력
현: Embedded 분야 SW Team leader
LG전자, VS사업부 IVI선행플랫폼/모듈개발
SW마에스트로, SW 멘토
강의경력
삼성전자, Qt & QML 강의
LG전자, Qt & QML 분야 사내 강사
한컴아카데미 Qt 강의 출강
다수의 IT기업 Qt 강의 출강
저서
Qt 프로그래밍
Qt Quick 프로그래밍
Qt5 프로그래밍 가이드
MeeGo 프로그래밍 완벽 가이드
Qt 실전 프로그래밍
SW커뮤니티 운영
Qt 개발자 커뮤니티 운영자 ( www.qt-dev.com )
All
80 lectures ∙ (11hr 55min)
Course Materials:
All
2 reviews
$59.40
Check out other courses by the instructor!
Explore other courses in the same field!