
Learn Terraform Basics with the Terraform Associate Exam
JeongSuk Lee
Learn the theory and practice of Terraform based on the HashiCorp Certified: Terraform Associate (003) exam content.
초급
Terraform
You will learn how to configure CI based on GitHub Actions and what content should be included in CI, and you can learn about verification through the SLSA Framework, which was a topic of discussion in Google DevOps Report 2022.
86 learners
Level Basic
Course period Unlimited

CI
GitHub Actions
SLSA Framework
InfraCost
Software Bill of Materials
SonarQube
TruffleHog
ConfTest
AWS IAM
Github Action for CI configuration!

"I'm curious about what CI is. How can I best grasp the concept from a technical perspective ?"
“My company has installed and is using a CI solution like Jenkins. What kind of content should I include in CI?”
“I received consulting on my CI/CD strategy, but I'm concerned about how to implement it .”
“We need to evaluate and manage our organization’s CI structure .”
When organizations talk about implementing CI, the actual implementation often involves only post-build package distribution. However, implementing CI involves establishing a software supply chain (SSC). It's not simply about installing a CI solution.
Learn how to configure Continuous Integration (CI) using Github Actions and how to apply the tools needed to configure the Software Supply Chain within CI.

This lecture covers the Model CI Flow , which must be implemented at a minimum when building a CI-based software supply chain. We hope this lecture will be helpful to those who have been curious about the standards and methods for building and evaluating CI systems.
Case 1 Are there any guidelines for configuring CI?
The SLSA Framework provides guidelines for the Software Supply Chain.
Case 2: In the CI system, there are concepts called Host and Agent. What are the ways to configure them?
We will explain how to configure the CI Host using Github Actions , and the Agent using either the SaaS-based Agent provided by Github or your own Agent based on the Ephemeral environment.
Case 3: I want to include our company's technical policy guidelines in CI. Is there a way to do this?
This article will explain how to apply security checks to CI using SonarQube and Aqua Trivy. It will also demonstrate Policy as Code (PoC) through ConfTest.
Case 4 Our organization uses IaC through Terraform. Can we manage the costs of this first in CI?
We'll explain how to use InfraCost to indicate cost increases or decreases for Terraform changes in GitHub Pull Requests.
CI isn't just about installing CI software and automating builds. Unlike typical CI courses that focus on builds and artifact creation, this course focuses on the core purpose of CI: Software Supply Chain Management and Gated Commit .
In addition, we will proceed by reflecting the latest trends such as Dependency management and SLSA Framework based on the Software Bill of Material, which has been highlighted due to recent security breaches caused by open source libraries (Log4j, SolarWind).
You'll understand that CI isn't just about installing CI software and automating builds. You'll also learn about the SLSA Framework and how it can be combined with other solutions to reach the highest Framework Level 4.
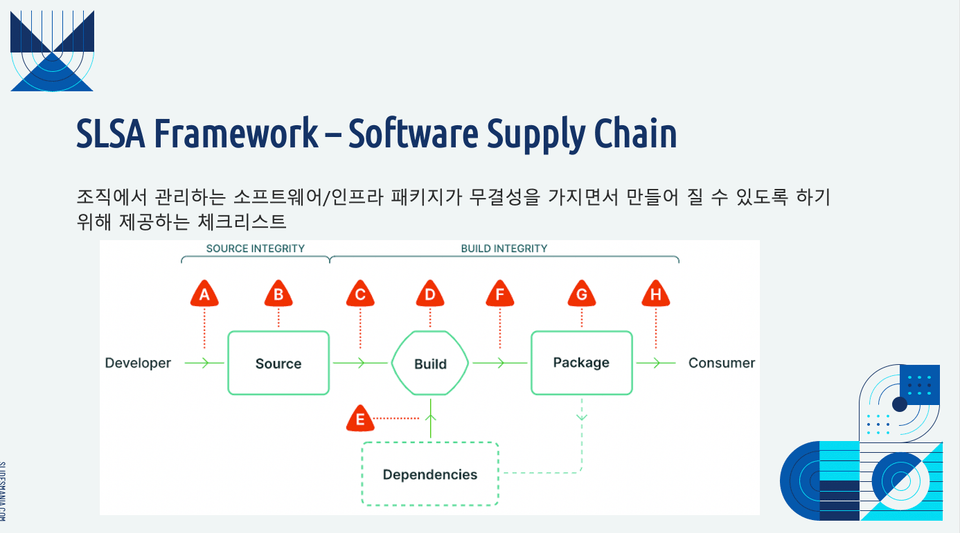
You'll learn how to implement Gated Commit using GitHub and explore how to build a CI chain for related services within a microservice architecture. You'll also learn how to create GitHub Custom Actions and leverage them to build a reusable software supply chain. You'll also understand the characteristics and differences between Persistent and Ephemeral agents.
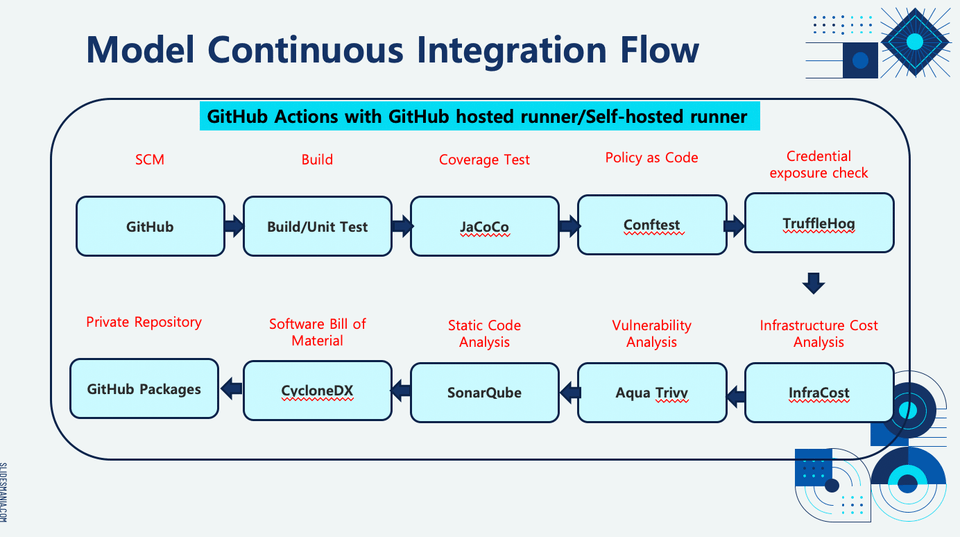
Getting Started with Github Actions
Verifying IaC Deployment Stability
Checking for security vulnerabilities in CI
Container image management using private repository
Modularizing the Build Process with GitHub Custom Actions
Implementing a GitHub Self-hosted Runner
Summary through SLSA Framework
I'm a digital nomad IT engineer with approximately 15 years of experience as a full-stack developer and DevOps engineer/consultant in Korea, Australia, and the UK. I'm constantly learning new topics to optimize IT organizational operations , and I dream of remaining an engineer until I retire. Currently, I work as a DevOps engineer on the Developer Experience team at a bank in Melbourne, Australia.
Q. When implementing CI, can't you just install Jenkins, enter the build command, and deploy it?
The goal of CI implementation isn't just to automate builds. Its purpose is to automate and review builds, tests, and organizational security/compliance requirements that may arise throughout the entire software supply chain, ensuring reliable artifacts are passed on to the CD team.
Q. I see you use a lot of software. Do I need any basic knowledge about it?
In this lecture, we will explain the purpose and method of use of the software used, and proceed with the process of integrating it with CI.
Q. How important is this part when building a career in DevOps?
In DevOps-related positions, CI/CD is a fundamental requirement, and questions about CI often ask for ideas or experience on how to structure pipelines. Pipeline flow and gated commits are crucial perspectives, and this lecture covers these aspects.
💾 Things to note before taking the class
The following PC specifications and service versions are required for this tutorial:
Who is this course right for?
For those of you who are curious about how to structure content within CI
For those who are completely new to GitHub Actions and want to gain basic knowledge
For those of you who are curious about how CI is configured in a Microservice Architecture
For those of you wondering how DevSecOps is configured in CI
Need to know before starting?
Shell Scripts
How to install Kubernetes environment, how to set up Minikube or EKS/GKE/AKS
How to install the Helm command
433
Learners
17
Reviews
7
Answers
3.7
Rating
7
Courses
I am a Digital Nomad IT Engineer with about 15 years of experience working as a Full-stack Developer and DevOps Engineer/Consultant in Korea, Australia, and the UK. I am constantly studying new topics to optimize the operation of IT organizations, and I have a dream of living as an engineer until I retire. Currently, I am working in DevOps within the Developer Experience team at a bank in Melbourne, Australia.
All
20 lectures ∙ (6hr 34min)
1. Overview
08:59
All
3 reviews
5.0
3 reviews
Reviews 6
∙
Average Rating 5.0
5
I think this lecture presents a starting point for realistic continuous integration that must be implemented in practice for development teams. Beyond simply running builds and unit tests, it condenses the cases and processes of configuring gated check-ins including static analysis, security, signing and publishing, and even feedback. Through this, unnecessary error codes are prevented from being extended to the source code, and it is naturally expected that this will effectively improve the collaboration of the development team. (Really, I was itching to refactor the CI process I am currently managing while listening to the lecture. ㅎㅎ) Above all, it is easy to get lost in the complex and numerous processes, but I am really grateful that the lecture course was organized and improved through the SLSA Framework. If you are taking this lecture for the first time, it would be a good idea to listen to the last session, 'Summary through SLSA Framework' after the first overview.
Reviews 2
∙
Average Rating 5.0
Reviews 1
∙
Average Rating 5.0
5
There were some difficult parts in taking this lecture because the systems I am currently developing and operating are legacy systems that run on the company data center. However, I was able to learn a lot other than Github Actions by looking at the various system connections and new development patterns introduced in this lecture. Unlike the general 101 lecture, I am grateful for the many comments from my rich experience that were very stimulating and helpful. Github Actions will be applied to GHE, which I will be managing in the future, and I think it will be very helpful. Thank you.
$152.90
Check out other courses by the instructor!
Explore other courses in the same field!