
AI Statistics for Non-Majors
arigaram
Without a single formula or line of code, this penetrates the essence of basic statistics necessary for AI development and application.
Beginner
AI
We introduce basic prompt patterns for coding and advanced API prompt patterns for leveraging artificial intelligence.

How to write prompts for development
Core development and documentation concepts, including Refactoring, TDD, BDD, Gherkin, and Cucumber.
This course is currently in the process of being completed. Please note that there is a downside of having to wait for a long time until the course is fully finished (although content will be added frequently). Please take this into consideration when making your purchase decision.
January 23, 2026
I have released the full table of contents for all lessons to be included in the specialized section.
With the full release of the professional section's table of contents, the course title has been changed from "Prompt Patterns (Vibe Coding) for Developers" to "Prompt Patterns for Developers" to make it more inclusive.
December 10, 2025
I have started posting the course content to be included in the Professional Section (Section 14 – Section 55).
November 30, 2025
Some of the sections within the advanced course have been categorized as professional sections. We plan to add more specialized lessons to these professional sections.
September 18, 2025
Added precautions to the detailed introduction page.
August 22, 2025
The detailed curriculum for the sections within the advanced course has been set to private. These sections will be made public individually as they are completed.
In this course, we explore how to write better prompts by introducing prompt engineering techniques necessary to make the most of various AI coding tools such as GPT, Copilot, ChatGPT, Claude, and Cursor.
Developers who write good prompts are faster and more competent.
Developers are no longer just people who write code.
In a development environment collaborating with AI, 'what to ask and how to ask it' has become a core competency.
We categorize prompt patterns by type and provide them along with real-world examples.
You can check the code generated by the prompt.
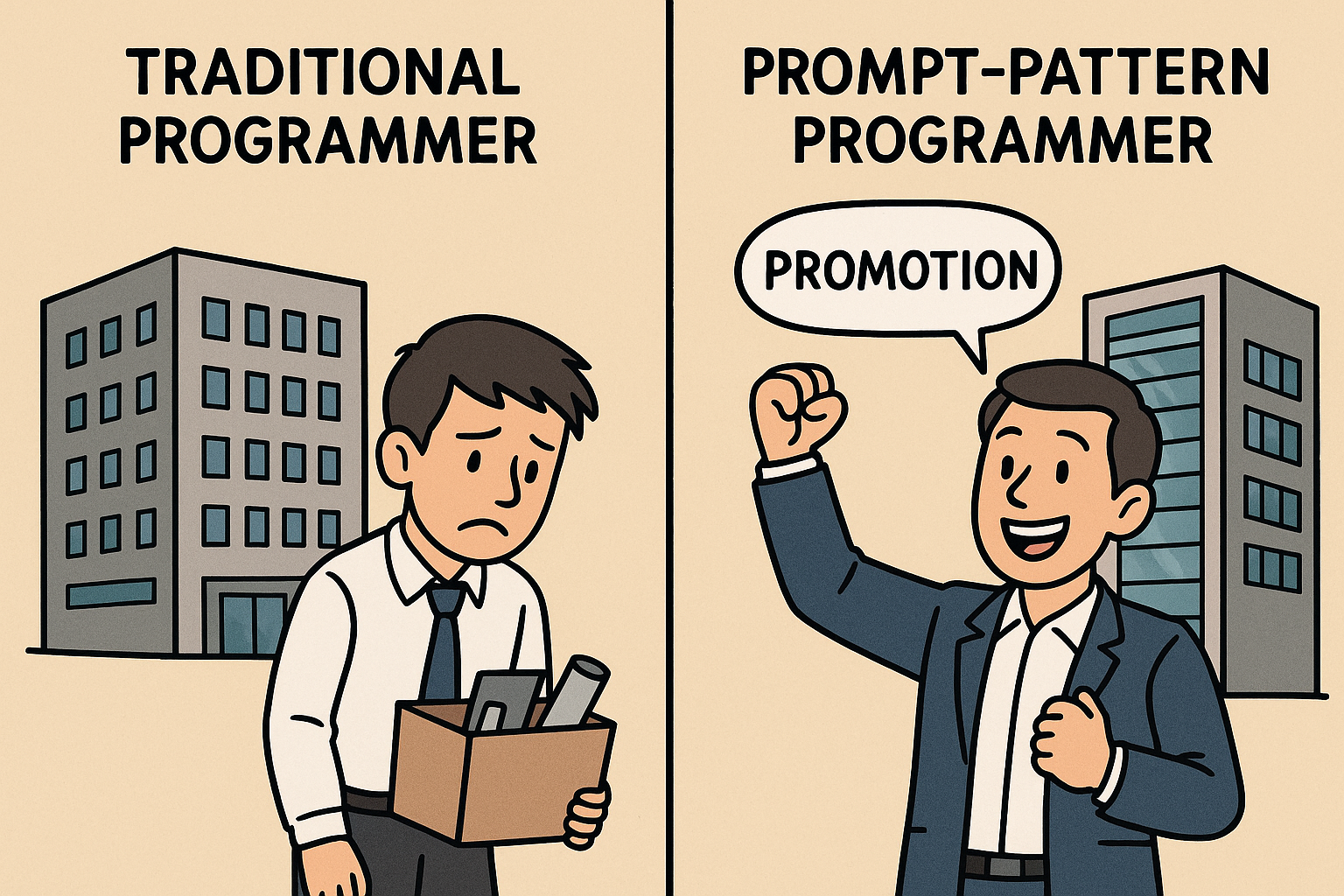
News reports frequently suggest that companies are no longer hiring junior developers and are even letting go of existing ones due to AI. Now is the time to transition from being a traditional programmer to a "Prompt Programmer"—one who utilizes prompt patterns.

Don't just stick to outdated development tools; actively leverage AI to significantly boost your productivity.
Developers with programming experience who are unfamiliar with using AI
Developers who spend a lot of time on repetitive coding, refactoring, and documentation tasks
Those who want to expand into new areas such as DevOps, data analysis, and security using prompts
Developers who can handle basic coding but lack habits for testing, refactoring, and documentation
Those who want to quickly adapt to practical work and grow into a “highly capable developer” through AI tools
Those who need to handle coding + infrastructure management + collaboration alone or in a small team with limited resources
Startup developers who need rapid prototyping and iterative experimentation
Those who are already using Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, etc., but want to strengthen data processing & visualization automation
Analysts interested in AI prompting → code automation → workflow optimization
Learners who want to quickly master new languages or frameworks
Researchers who want to accelerate the technical paper summarization → code reproduction process with the help of AI
Those who want to understand prompt-based code review/quality control/automation workflows while collaborating with development teams
Those who want to streamline collaboration between planners, designers, and developers
Key Topics: Why prompts are important for developers, changing work structures, and basic concepts.
Lessons covered: Importance, definition of a good prompt, factors to consider when writing, the value of patterns, etc.
Key Topic: Basic patterns for requesting actual functional code from AI.
Lessons covered: CRUD, UI components, state management, event handling, asynchronous, framework-based requests.
Key Topic: Requests for improving and structuring existing code.
Lessons covered: Improving readability, function extraction, removing duplication, OOP conversion, immutability, performance improvement.
Key Theme: Ensuring quality through test automation.
Lessons covered: Unit/integration testing, edge cases, mock/stub, TDD style, coverage expansion.
Core Theme: Automation of comments, API documentation, READMEs, and change logs.
Lessons covered: Function comments, docstring, JSDoc/TSDoc, technical blogs, API documentation, changelog summaries.
Key Topic: Automating conversion between languages and frameworks.
Lessons covered: JS↔TS, Python 2↔3, Java↔Kotlin, jQuery↔React, REST↔GraphQL, SQL↔NoSQL.
Key Theme: Code interpretation and error detection through AI.
Lessons covered: Code explanation, complex logic interpretation, complexity analysis, security issues, and debugging log automation.
thought Key Topic: Applying consistent code styles.
Lessons covered: ESLint, PEP8, Prettier, custom rules, semicolon/indentation conventions.
thought Key Theme: Project-based prompt utilization.
Lessons covered: Prompt chaining, iterative improvement strategies, collaboration standardization.
Core Topics: Data Preprocessing, Analysis, and Visualization.
Lessons covered: Pandas/Numpy preprocessing, visualization, efficient large-scale data processing, CSV/JSON/XML parsing, and log analysis automation.
Key Topic: Infrastructure code automation through AI.
Lessons covered: Dockerfile, Kubernetes manifests, CI/CD pipelines, Terraform/CDK, server configuration files.
Key Topics: Security vulnerabilities and quality assurance.
Lessons covered: Vulnerability scanning, static analysis, API key management, load testing, security log automation.
Core Topic: Combined use of images, voice, and documents.
Lessons covered: Image→Code, Voice Command→Code, Figma→UI Code, Document Summary+Code, Multimodal Workflow.
Key Theme: Managing and automating prompts themselves.
Lessons Covered: Templatization, LangChain, Performance Benchmarking, Zapier/n8n, Tool-based Agents.
Core Theme: Team-level prompt utilization strategies.
Lessons covered: Code review automation, team convention-based prompts, Jira/Notion integration, history management, and cross-functional collaboration.
Key Topic: Prompts for self-learning and research.
Lessons covered: Tutorial generation, open-source exploration, paper summary to code, algorithm learning, and learning roadmap automation.
Key Topic: Utilization in the service operation phase.
Lessons covered: Failure analysis, log-based error detection, performance monitoring, batch scripts, and emergency patch code.
Key Topic: Improving User Experience.
Lessons covered: Accessibility standards, multilingual i18n, incorporating user feedback, A/B testing code, UI animation.
Key Topic: Industry-specific customized prompts.
Lessons covered: Game development, financial data, medical data protection, e-commerce, IoT/embedded.
Key Theme: Responsible AI Development.
Lessons Covered: PII de-identification, data bias verification, copyright and license review, secure input handling, and ethical code review.
The ability to utilize prompts to boost coding productivity by 2 to 3 times
Prompt templates for automating repetitive tasks
A foundation for prompt standardization that can be shared with team members
Hands-on experience with prompts that can be applied immediately to real-world projects
Future competitiveness as a "developer collaborating with AI"
You just need to prepare one of the AI-based coding tools such as ChatGPT, Gemini, Grok, Claude, or Copilot.
The lecture notes are attached in PDF format.
The explanations are provided using JavaScript and Python, so it is helpful to have a basic knowledge of these two languages.
It will be very helpful if you have a basic understanding of refactoring. In this regard, my separate course, "Clean Coding: Techniques for Writing Good Code Explained Easily Through Cooking Analogies," will also serve as a great reference.
Who is this course right for?
Those who want to develop faster and more accurately using AI tools
Those who want to use ChatGPT or Copilot effectively but feel lost on what to ask and how to ask it.
Those who want to automate repetitive development tasks using prompts
Developers who want to collect prompt examples that can be used immediately in practice.
A manager looking to introduce a culture of AI prompting to their team
Need to know before starting?
Python language
Refactoring
JavaScript language
613
Learners
31
Reviews
2
Answers
4.5
Rating
18
Courses
I am someone for whom IT is both a hobby and a profession.
I have a diverse background in writing, translation, consulting, development, and lecturing.
All
287 lectures ∙ (44hr 22min)
Course Materials:
All
5 reviews
4.4
5 reviews
Reviews 1
∙
Average Rating 5.0
Reviews 6
∙
Average Rating 5.0
Reviews 4
∙
Average Rating 5.0
Reviews 1
∙
Average Rating 2.0
$77.00
Check out other courses by the instructor!
Explore other courses in the same field!