
인프런 워밍업 클럽 4기 CS 전공지식 2주차 발자국
[컴퓨터 구조]
멀티플렉서 (Multiplexer, MUX)
여러 개의 입력 중 하나를 선택해 출력하는 회로
2^n개의 입력 →1개의 출력선택 신호(Select Line)로 출력 결정
예: 4:1 MUX는 입력 4개, 출력 1개, 선택선 2개
주요 역할: 다수의 데이터 중 필요한 것만 선택
디멀티플렉서 (Demultiplexer, DEMUX)
하나의 입력을 선택된 출력 하나로 전달하는 회로
1개의 입력 →2^n개의 출력선택 신호로 어느 출력으로 보낼지 결정
주요 역할: 하나의 데이터를 여러 대상 중 하나로 분배
디코더 (Decoder)
n개의 입력을 받아 2^n개의 출력 중 하나를 활성화특정 입력 조합 → 해당 출력 하나만 1(활성화), 나머지는 0
예: 3→8 디코더는 입력 3개 → 출력 8개
주요 역할: 특정 주소 또는 명령어를 구분해 선택
컨트롤 버퍼 (Control Buffer)
제어 신호(Control Signal) 또는 제어 정보(Control Data)를 일시 저장하거나 전달하는 버퍼 회로
CPU 내부, 메모리 컨트롤러, I/O 디바이스 제어 등에서 사용
동기화, 속도 차 완충, 임시 저장, 전달 안정화 등의 역할 수행
경우에 따라 컨트롤 레지스터(Control Register) 와 혼용되기도 함
주요 역할:
제어 신호의 전달 시 타이밍 조절
동기화 문제 해결
제어 흐름의 안정성 유지
반가산기 (Half Adder)
두 개의 1비트 이진수(A, B)를 더하는 회로
출력: 합(Sum), 자리올림(Carry)
논리식:
Sum = A ⊕ BCarry = A ∧ B
특징: 이전 자리에서의 올림값(Carry-in)을 처리할 수 없음
전가산기 (Full Adder)
세 개의 1비트 이진수(A, B, Carry-in)를 더하는 회로
출력: 합(Sum), 자리올림(Carry-out)
논리식:
Sum = A ⊕ B ⊕ CinCout = (A ∧ B) ∨ (B ∧ Cin) ∨ (A ∧ Cin)
특징: 자리올림 입력을 처리할 수 있어 다비트 덧셈 가능
조합 논리 회로 (Combinational Logic Circuit)
현재 입력에만 의존하여 출력이 결정되는 회로
과거 상태(기억)를 고려하지 않음 → 메모리 없음
출력 = 입력의 조합 결과
특징:
입력이 바뀌면 출력이 즉시 바뀜
클럭 신호 불필요
대표 예시:
가산기(Adder), 디코더(Decoder), 인코더(Encoder), 멀티플렉서(MUX), 비교기 등
순차 논리 회로 (Sequential Logic Circuit)
입력 + 현재 상태(과거 출력)에 따라 출력이 결정
기억 기능(메모리) 포함
클럭(Clock) 신호 사용 → 타이밍 기반 동작
특징:
출력이 시간의 흐름에 따라 달라짐
상태를 저장하고 변화함 (플립플롭, 레지스터 등 포함)
대표 예시:
플립플롭(Flip-Flop), 레지스터(Register), 카운터(Counter), FSM(상태 기계), 메모리 등
SR 래치 (Set-Reset Latch)
S(Set), R(Reset) 두 입력으로 출력 Q 제어
출력은 이전 상태를 기억함 (순차 회로의 기본 형태)
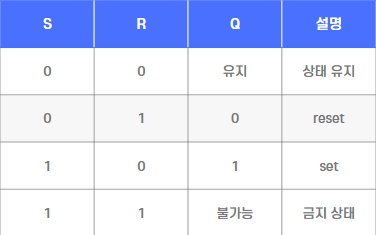
문제점: S=1, R=1이면 출력이 불안정해짐
D 래치 (Data or Delay Latch)
SR 래치의 문제(S=1, R=1)를 해결하기 위해 설계
입력: D(Data), Enable (또는 Clock)
Enable이 1일 때만 D값이 Q로 전달됨
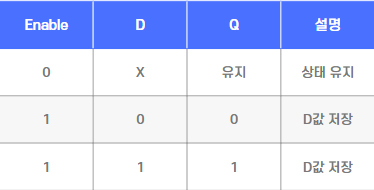
특징: 항상 안정적인 동작, 메모리 소자에 많이 사용
JK 래치
SR 래치의 금지 상태를 해결한 구조
입력: J, K, Clock
J: Set 역할, K: Reset 역할
J=K=1이면 출력 반전
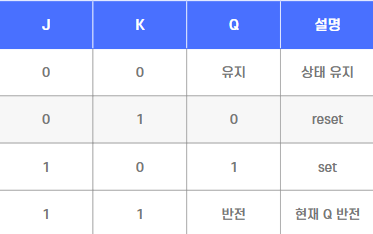
특징: 플립플롭 구현에 주로 사용됨
클럭 (Clock)
디지털 회로에서 동기 신호를 제공하는 주기적인 펄스
회로 동작의 타이밍 기준 역할
클럭 상승엣지(↑), 하강엣지(↓)에서 동작하도록 회로 설계됨
플립플롭 (Flip-Flop)
1비트의 정보를 저장할 수 있는 순차 논리 회로
클럭에 의해 상태가 변하거나 유지됨
D, JK, T 등 여러 종류가 있음
레지스터 (Register)
여러 개의 플립플롭을 묶은 구조 (보통 8, 16, 32비트 등)
CPU 내부에서 데이터를 임시 저장하는 데 사용
동기식으로 동작하며 고속 처리 가능
RAM (Random Access Memory)
데이터를 읽고 쓰기 가능한 임의 접근 메모리
전원이 꺼지면 데이터가 사라짐(휘발성)
주소 지정으로 원하는 위치의 데이터를 직접 접근
[자료구조와 알고리즘]
강의 수강
나의 주력 언어는 c++이라서 강의를 토대로 c++버젼으로 바꿔보았다
Red-Black Tree
자기 균형 이진 탐색 트리(BST)의 일종
삽입/삭제 시 균형 유지를 위한 색상(빨강/검정) 속성 사용
Red-Black Tree의 주요 특징
노드는 빨강(Red) 또는 검정(Black)
루트 노드는 항상 검정
모든 리프(NIL)는 검정 (NULL 노드 포함)
빨간 노드의 자식은 반드시 검정 (연속된 빨강 없음)
임의의 노드에서 리프까지 가는 모든 경로에는 동일한 수의 검정 노드 존재
Red-Black Tree의 장점
AVL Tree보다 회전 횟수가 적음
삽입/삭제 성능이 더 안정적임
Red-Black Tree의 단점
AVL보다 탐색 시간이 조금 느림 (균형이 느슨함)
시간 복잡도
탐색 / 삽입 / 삭제: O(log n)
최악의 경우에도 높이가 log₂(n) 이내로 유지됨
Red_BlackTree.h
#pragma once
#include "BinarySearchTree.h"
// Red-Blakc Tree
// 1) 모든 노드는 Red or Black
// 2) Root는 Black
// 3) Leaf(NIL)는 Black
// 4) Red 노드의 자식은 Black (연속해서 Red-Red X)
// 5) 각 노드로부터 ~ 리프까지 가는 경로들은 모두 같은 수의 Black
class Red_BlackTree
{
public:
Red_BlackTree();
~Red_BlackTree();
void Print();
void Print(Node* node, int x, int y);
Node* Search(Node* node, int key);
Node* Min(Node* node);
Node* Max(Node* node);
Node* Next(Node* node);
void Insert(int key);
void InsertFixup(Node* node);
void Delete(int key);
void Delete(Node* node);
void DeleteFixup(Node* node);
void Replace(Node* u, Node* v);
// Red-Black Tree
void RotateLeft(Node* node);
void RotateRight(Node* node);
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
Node* _nil = nullptr;
};Red_BlackTree.cpp
#include "Red_BlackTree.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
using namespace std;
enum class ConsoleColor
{
BlACK = 0,
RED = FOREGROUND_RED,
GREEN = FOREGROUND_GREEN,
BLUE = FOREGROUND_BLUE,
YELLOW = RED | GREEN,
WHITE = RED | GREEN | BLUE,
};
void SetCursorColor(ConsoleColor color)
{
HANDLE output = ::GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
::SetConsoleTextAttribute(output, static_cast<SHORT>(color));
}
void SetCursorPosition(int x, int y)
{
HANDLE output = ::GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
COORD pos = { static_cast<SHORT>(x), static_cast<SHORT>(y) };
::SetConsoleCursorPosition(output, pos);
}
void ShowConsoleCursor(bool flag)
{
HANDLE output = ::GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
CONSOLE_CURSOR_INFO cursorInfo;
::GetConsoleCursorInfo(output, &cursorInfo);
cursorInfo.bVisible = flag;
::SetConsoleCursorInfo(output, &cursorInfo);
}
Red_BlackTree::Red_BlackTree()
{
_nil = new Node(); // Black
_root = _nil;
_root->parent = _nil;
}
Red_BlackTree::~Red_BlackTree()
{
delete _nil;
}
void Red_BlackTree::Print()
{
::system("cls");
ShowConsoleCursor(false);
Print(_root, 10, 0);
}
void Red_BlackTree::Print(Node* node, int x, int y)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return;
SetCursorPosition(x, y);
if (node->color == Color::Black)
SetCursorColor(ConsoleColor::BLUE);
else
SetCursorColor(ConsoleColor::RED);
cout << node->key;
Print(node->left, x - (5 / (y + 1)), y + 1);
Print(node->right, x + (5 / (y + 1)), y + 1);
SetCursorColor(ConsoleColor::WHITE);
}
Node* Red_BlackTree::Search(Node* node, int key)
{
if (node == _nil || key == node->key)
return node;
if (key < node->key)
return Search(node->left, key);
else
return Search(node->right, key);
}
Node* Red_BlackTree::Min(Node* node)
{
while (node->left != _nil)
node = node->left;
return node;
}
Node* Red_BlackTree::Max(Node* node)
{
while (node->right != _nil)
node = node->right;
return node;
}
Node* Red_BlackTree::Next(Node* node)
{
if (node->right != _nil)
return Min(node->right);
Node* parent = node->parent;
while (parent != _nil && node == parent->right)
{
node = parent;
parent = parent->parent;
}
return parent;
}
void Red_BlackTree::Insert(int key)
{
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->key = key;
Node* node = _root;
Node* parent = _nil;
while (node != _nil)
{
parent = node;
if (key < node->key)
node = node->left;
else
node = node->right;
}
newNode->parent = parent;
if (parent == _nil)
_root = newNode;
else if (key < parent->key)
parent->left = newNode;
else
parent->right = newNode;
// 검사
newNode->left = _nil;
newNode->right = _nil;
newNode->color = Color::Red;
InsertFixup(newNode);
}
void Red_BlackTree::InsertFixup(Node* node)
{
// 1) p = red, uncle = red
// -> p = black, uncle = black, pp = red로 바꿈
// 2) p = red, uncle = black (triangle)
// -> 회전을 통해 case 3으로 바꿈
// 3) p = red, uncle = black (list)
// -> 색상 변경 + 회전
while (node->parent->color == Color::Red)
{
if (node->parent == node->parent->parent->left)
{
Node* uncle = node->parent->parent->right;
if (uncle->color == Color::Red) // p = red, uncle = red
{
node->parent->color = Color::Black; // p
uncle->color = Color::Black; // u
node->parent->parent->color = Color::Red;
node = node->parent->parent;
}
else // p = red, uncle = black
{
if (node == node->parent->right)
{
// Triangle 타입
// [pp(B)]
// [p(R)] [u(B)]
// [n(R)]
// [pp(B)]
// [p(R)] [u(B)]
// [n(R)]
node = node->parent;
RotateLeft(node);
}
// List 타입
// [pp(R)]
// [p(B)] [u(B)]
// [n(R)]
// [p(B)]
// [n(R)] [pp(R)]
// [u(B)]
node->parent->color = Color::Black;
node->parent->parent->color = Color::Red;
RotateRight(node->parent->parent);
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = node->parent->parent->left;
if (uncle->color == Color::Red) // p = red, uncle = red
{
node->parent->color = Color::Black; // p
uncle->color = Color::Black; // u
node->parent->parent->color = Color::Red;
node = node->parent->parent;
}
else // p = red, uncle = black
{
if (node == node->parent->left)
{
node = node->parent;
RotateRight(node);
}
// List 타입
// [p(B)]
// [pp(R)] [n(R)]
// [u(B)]
node->parent->color = Color::Black;
node->parent->parent->color = Color::Red;
RotateLeft(node->parent->parent);
}
}
}
_root->color = Color::Black;
}
void Red_BlackTree::Delete(int key)
{
Node* deleteNode = Search(_root, key);
Delete(deleteNode);
}
// 먼저 BST 삭제 실행
void Red_BlackTree::Delete(Node* node)
{
if (node == _nil)
return;
if (node->left == _nil)
{
Color color = node->color;
Node* right = node->right;
Replace(node, node->right);
if (color == Color::Black)
DeleteFixup(right);
}
else if (node->right == _nil)
{
Color color = node->color;
Node* left = node->left;
Replace(node, node->left);
if (color == Color::Black)
DeleteFixup(left);
}
else
{
// 다음 데이터 찾기
Node* next = Next(node);
node->key = next->key;
Delete(next);
}
}
// 먼저 BST 삭제 실행...
// - Case 1) 삭제할 노드가 Red-> 그냥 삭제! 끝!
// - Case 2) root가 DB -> 그냥 추가 Black 삭제! 끝!
// - Case 3) DB의 sibling 노드가 Red
// -- s = black, p = red (s <-> p 색상 교환)
// -- DB 방향으로 rotate(p)
// -- goto other case
// - Case 4) DB의 sibling 노드가 Black && sibling의 양쪽 자식도 Black
// -- 추가 Black을 parent에게 이전
// --- p가 Red이면 Black 됨.
// --- p가 Black이면 DB 됨.
// -- s = red
// -- p를 대상으로 알고리즘 이어서 실행 (DB가 여전히 존재하면)
// - Case 5) DB의 sibling 노드가 Black && sibling의 near child = red, far child = black
// -- s <-> near 색상 교환
// -- far 방향으로 rotate(s)
// -- goto case 6
// - Case 6) DB의 sibling 노드가 Black && sibling의 far child = red
// - p <-> s 색상 교환
// - far = black
// - rotate(p) (DB 방향으로)
// - 추가 Black 제거
void Red_BlackTree::DeleteFixup(Node* node)
{
Node* x = node;
// [Case 1][Case 2]
while (x != _root && x->color == Color::Black)
{
// [p(B)]
// [x(DB)] [s(R)]
// [1]
// [S(B)]
// [p(R)]
// [x[DB] [1]
if (x == x->parent->left)
{
Node* s = x->parent->right;
// [Case 3]
if (s->color == Color::Red)
{
s->color = Color::Black;
x->parent->color = Color::Red;
RotateLeft(x->parent);
s = x->parent->right;
}
// [Case 4]
if (s->left->color == Color::Black &&
s->right->color == Color::Black)
{
s->color = Color::Red;
x = x->parent;
}
else
{
// [Case 5]
// [p]
// [x(DB)] [s(B)]
// [near(R)] [far(B)]
// [p]
// [x(DB)] [near(B)]
// [s(R)]
// [far(B)]
if (s->right->color == Color::Black)
{
s->left->color == Color::Black;
s->color == Color::Red;
RotateRight(s);
s = x->parent->right; // near
}
// [Case 6]
// [p]
// [x(DB)] [s(B)]
// [far(R)]
s->color = x->parent->color;
x->parent->color = Color::Black;
s->right->color = Color::Black;
RotateLeft(x->parent);
x = _root; // 루프를 빠져나오기 위해서
}
}
else
{
// [Case3]
Node* s = x->parent->left;
if (s->color == Color::Red)
{
s->color = Color::Black;
x->parent->color = Color::Red;
RotateRight(x->parent);
s = x->parent->left; // [1]
}
// [Case4]
if (s->right->color == Color::Black && s->left->color == Color::Black)
{
s->color = Color::Red;
x = x->parent;
}
else
{
// [Case5]
if (s->left->color == Color::Black)
{
s->right->color = Color::Black;
s->color = Color::Red;
RotateLeft(s);
s = x->parent->left;
}
// [Case6]
s->color = x->parent->color;
x->parent->color = Color::Black;
s->left->color = Color::Black;
RotateRight(x->parent);
x = _root;
}
}
}
x->color = Color::Black;
}
// u 서브트리를 v 서브트리로 교체
// 그리고 delete u
void Red_BlackTree::Replace(Node* u, Node* v)
{
if (u->parent == _nil)
_root = v;
else if (u == u->parent->left)
u->parent->left = v;
else
u->parent->right = v;
v->parent = u->parent;
delete u;
}
// [x]
// [1] [y]
// [2][3]
// [y]
// [x] [3]
// [1][2]
void Red_BlackTree::RotateLeft(Node* x)
{
Node* y = x->right;
x->right = y->left;
if (y->left != _nil)
y->left->parent = x;
y->parent = x->parent;
if (x->parent == _nil)
_root = y;
else if (x == x->parent->left)
x->parent->left = y;
else
x->parent->right = y;
y->left = x;
x->parent = y;
}
// [y]
// [x] [3]
// [1][2]
// [x]
// [1] [y]
// [2][3]
void Red_BlackTree::RotateRight(Node* y)
{
Node* x = y->left;
y->left = x->right;
if (x->right != _nil)
x->right->parent = y;
x->parent = y->parent;
if (y->parent == _nil)
_root = x;
else if (y == y->parent->right)
y->parent->right = x;
else
y->parent->left = x;
x->right = y;
y->parent = x;
}
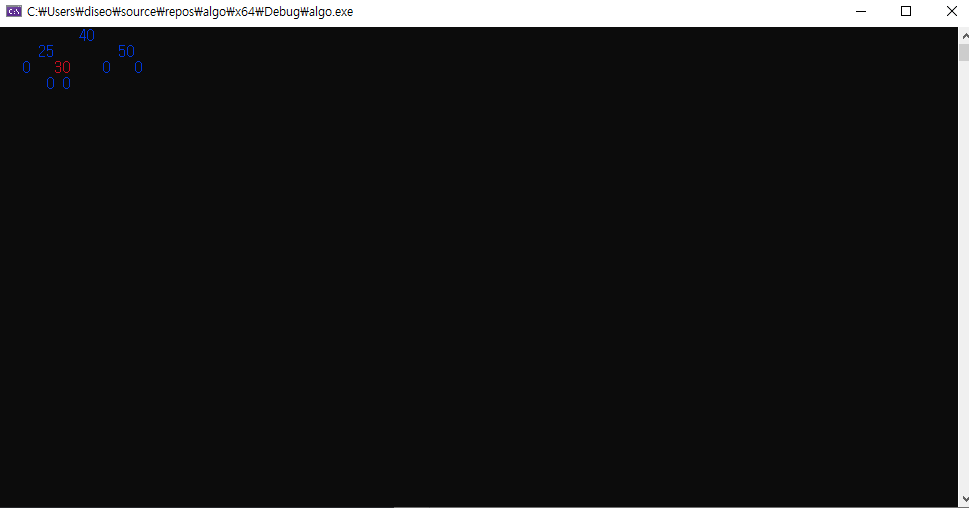
출력 결과
int main()
{
Red_BlackTree rbt;
rbt.Insert(30);
rbt.Print();
//this_thread::sleep_for(1s);
rbt.Insert(10);
rbt.Print();
//this_thread::sleep_for(1s);
rbt.Insert(20);
rbt.Print();
//this_thread::sleep_for(1s);
rbt.Insert(25);
rbt.Print();
//this_thread::sleep_for(1s);
rbt.Insert(40);
rbt.Print();
//this_thread::sleep_for(1s);
rbt.Insert(50);
rbt.Print();
//this_thread::sleep_for(1s);
rbt.Delete(20);
rbt.Print();
this_thread::sleep_for(1s);
rbt.Delete(10);
rbt.Print();
this_thread::sleep_for(1s);
}
우선순위 큐와 힙
우선순위 큐 (Priority Queue)
일반 큐와 달리, 요소들이 삽입된 순서가 아니라 우선순위에 따라 처리됨
가장 높은 우선순위의 요소가 먼저 나감
삽입(Push)과 삭제(Pop)에 평균 O(log n) 시간복잡도
내부 구현은 보통 힙(Heap) 자료구조로 되어 있음
사용 예:
CPU 스케줄러
다익스트라 알고리즘
이벤트 처리 시스템
힙 (Heap)
완전 이진 트리의 일종
부모 노드가 자식 노드보다 항상 우선순위가 높거나 낮은 특성을 가짐
두 종류가 있음:
최대 힙 (Max Heap): 부모 ≥ 자식 → 가장 큰 값이 루트
최소 힙 (Min Heap): 부모 ≤ 자식 → 가장 작은 값이 루트
삽입: 마지막 위치에 추가 후 위로 올라가며 정렬 (Heapify-up)
삭제: 루트 제거 후 마지막 노드를 루트로 옮기고 아래로 정렬 (Heapify-down)
시간복잡도
삽입: O(log n)
삭제: O(log n)
최대/최솟값 조회: O(1)
힙 정렬
완전 이진 트리 기반 정렬 알고리즘
최대 힙(Max Heap) 또는 최소 힙(Min Heap)을 이용
제자리 정렬 가능 (in-place), 안정 정렬은 아님
동작 과정
배열을 힙 구조로 만든다 (heapify)
루트(최대/최소값)를 배열 끝으로 보내고 힙 크기 감소
나머지 트리를 다시 heapify
이 과정을 배열 전체 크기만큼 반복
시간 복잡도
힙 구성: O(n)
정렬(heapify 반복): O(n log n)
총 시간 복잡도: O(n log n) (최악/최선/평균 동일)
PriorityQueue.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
template<typename T, typename Container = vector<T>, typename Predicate = less<T>>
class PriorityQueue
{
public:
void push(const T& data)
{
// 우선 힙 구조부터 맞춰준다
_heap.push_back(data);
// 도장깨기 시작
int now = static_cast<int>(_heap.size()) - 1;
// 루트 노드까지
while (now > 0)
{
// 부모 노드와 비교
int next = (now - 1) / 2;
if (_predicate(_heap[now], _heap[next]))
break;
// 데이터 교체
::swap(_heap[now], _heap[next]);
now = next;
}
}
void pop()
{
// 맨 뒤에값 루트로 교체 후 맨 뒤값 제거
_heap[0] = _heap.back();
_heap.pop_back();
int now = 0;
while (true)
{
int left = 2 * now + 1;
int right = 2 * now + 2;
// 리프에 도달한 경우
if (left >= (int)_heap.size())
break;
int next = now;
// 왼쪽과 비교
if (_predicate(_heap[next], _heap[left]))
next = left;
// 둘 중 승자를 오른쪽과 비교
if (right < (int)_heap.size() && _predicate(_heap[next], _heap[right]))
next = right;
// 왼쪽,오른쪽 둘 다 현재 값보다 작으면 종료
if (next == now)
break;
::swap(_heap[now], _heap[next]);
now = next;
}
}
T& top()
{
return _heap[0];
}
bool empty()
{
return _heap.empty();
}
private:
Container _heap = {};
Predicate _predicate = {};
};
출력 결과
int main()
{
PriorityQueue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq;
//PriorityQueue<int, vector<int>> pq;
pq.push(100);
pq.push(300);
pq.push(200);
pq.push(500);
pq.push(400);
while (pq.empty() == false)
{
int value = pq.top();
pq.pop();
cout << value << endl;
}
}
댓글을 작성해보세요.
